We are committed to solving the problems of lack of quantitative methods, complex operation and large errors in existing wettability tests, aiming to accurately measure the wetting rate of materials such as pole pieces and diaphragms
Application Areas
![]()
·Performance evaluation of electrolytes and related solvents
Monitor the penetration rate of electrolyte in the electrode
Solvent compatibility verification
·Optimization of liquid absorption performance of positive and negative pole pieces
·Evaluation and selection of isolation membrane wettability
Evaluate the matching of diaphragm porosity and pole piece pore structure
Simultaneous dual channel measurement |
PCT Patent Technology |
One-stop data collection |
With visual detection and recording function |
Compatible with liquid suction weight monitoring |
Closed environment chamber |
Model | Wet 01 | Wet 20R | |
Number of channels | 1 | 2 | |
Test Principle | Pendant drop contact angle method | Weighing method | |
Visual assistance system | √ | √ | |
Test platform auxiliary system | √ | √ | |
Injection control | Range | 2~10μL | 0~50mL |
Accuracy | ±0.1μL | ±1mL | |
Contact angle measurement | Range | 0~180° x | x |
Accuracy | ±1° | x | |
Weight measurement | Range | x | 0-220g |
Accuracy | x | ±1mg | |
Resolution | x | 0.1mg | |
Servo motion control | Motion Motor | Servo Motor | |
Rated load rate | 1~20mm/s | ||
Positioning accuracy | ±0.01mm | ||
Instrument size | ~300*310*540mm | ~610*600*650mm | |
Instrument weight | 25kg | 28kg | |
The electrode wettability refers to the wetting ability between the electrolyte and the surface of the positive and negative electrodes. It is related to the uniformity of electrolyte penetration inside the electrode and is a key indicator affecting the battery's charging and discharging efficiency, cycle life and safety performance.
Wettability Test Method Development |
·Drop method
· Capillary drop method
·Contact angle method
· Ultrasonic method
· Weighing method
· Resistance method
The impact of poor wettability of the electrode |
·Uneven electrolyte penetration
·Decreased structural stability
·Abnormal SEI film formation
Impact on batteries |
·Battery cell capacity
·Battery cell cycle life
·Battery cell safety
·Battery pack consistency
Gravimetric method As the electrolyte continues to infiltrate the coating, the precision mass/resistance module monitors the changes in the electrode resistance. The system processes the mass/resistance change rate and amount in real time. The change time and amount reflect the electrolyte infiltration rate of the electrode, and the change curve reflects the difference in the electrode pore curvature, so that the electrode pore consistency can be evaluated.
| Contact angle method The contact angle method evaluates the wettability of the electrode by measuring the contact angle (θ) formed by the electrolyte droplet on the electrode surface. The smaller the contact angle (θ < 65°), the better the electrode's lyophilicity and the faster the electrolyte penetration rate; the larger the contact angle (θ > 65°), the stronger the lyophobicity and the poorer the penetration ability.
|
Integration The first fully integrated gas production pressure measurement device The industry leader promotes the product | Ultra-wide temperature range -40°C~250°C ultra-wide measurement temperature range Unique buffer structure design prevents electrolyte from contacting and corroding the sensor | Fully automatic measurement One-stop multi-channel, new measurement experience Fully automatic measurement of all parameters | Professional data processing Single point mode and linear mode are optional Measurement data is displayed online in real time |
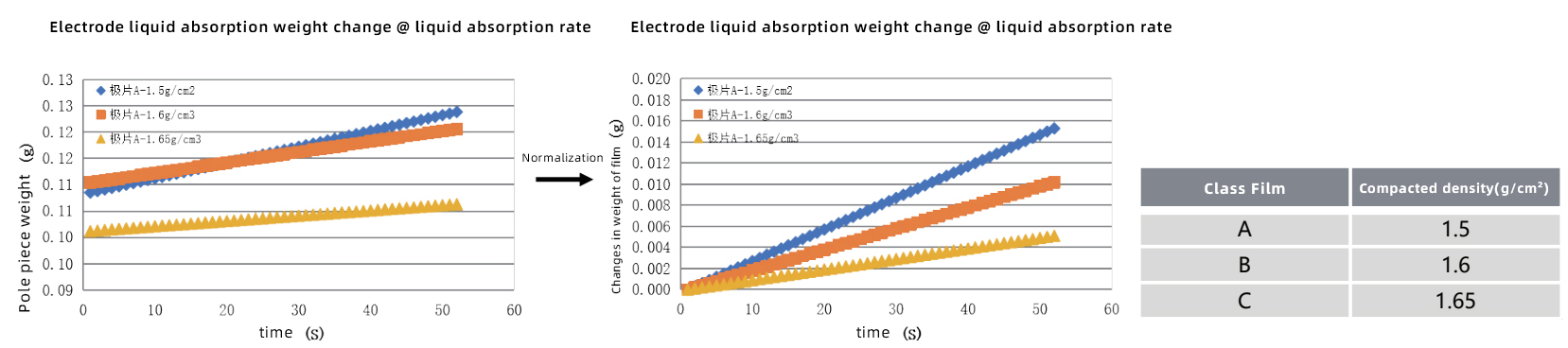
1. Analysis of the difference in liquid absorption of anode plates with different compaction |
The infiltration amount of different pole pieces at each time point shows a decreasing trend with the increase of compaction density, and the wettability of the pole pieces shows a good linear relationship with the increase of compaction density.
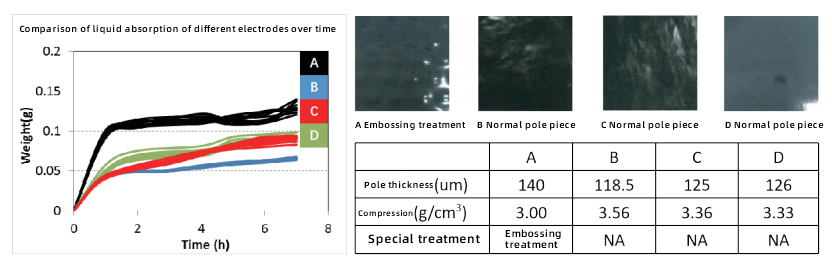
2. Analysis of the difference in liquid absorption of cathode plates with different compaction |
·After embossing treatment, the liquid absorption capacity of the electrode is significantly enhanced; the greater the compaction density, the slower the liquid absorption rate;
·Study the effects of different treatments (such as embossing) and compaction density on the liquid absorption performance of battery electrodes to optimize the electrode manufacturing process.
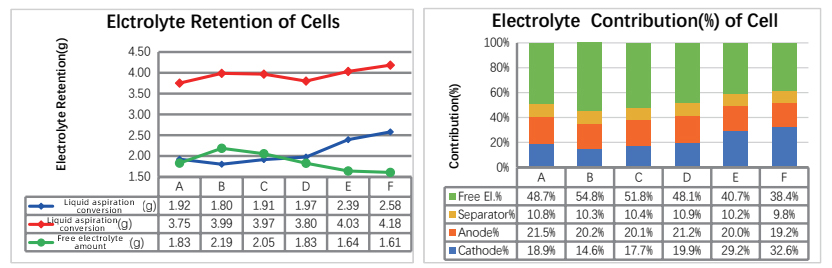
3. Analysis of liquid absorption differences in high silicon anode + LFMP doped LCO system |
·LFMP doping significantly improves the electrode's liquid absorption capacity;
·Electrolyte distribution characteristics: The diaphragm contributes about 10%, the free electrolyte accounts for up to 50%, and the anode contribution (~20%) is significantly higher than the cathode (~10%); the effect of different LFMP doping amounts on the electrode wettability and the distribution of the electrolyte in the battery cell are studied.
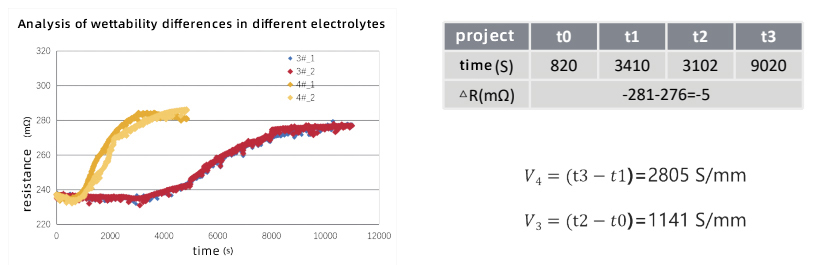
4.Analysis of wettability differences in different electrolytes |
·Electrolyte wetting rate: 4# electrolyte>3# electrolyte
·By comparing the wettability of different electrolytes on the same negative electrode sheet, the effect of electrolyte formula on wetting rate and electrode sheet resistance is explored.