We are committed to solving the problems of lack of reliable methods, non-standardization, offline non-in-situ, data independence, etc., and realize high-precision in-situ monitoring of battery cell volume expansion and gas production rate
Application Areas
![]()
·Material development
Electrolyte formula screening, positive and negative electrode material evaluation
·Process development
Formation process optimization, packaging pressure verification
·Abuse evaluation
Simulation of abuse scenarios to achieve risk assessment
·Cycling reliability evaluation
Irreversible expansion analysis rate impact evaluation
All-in-one |
Multi-parameter one-stop collection |
Fully automatic measurement |
Real-time online display of measurement data |
Multiple measurement modes |
Hybrid equipment, electrochemical mass spectrometer, gas chromatography, etc. |
Model | CVR110 | CVH100 | CVH200 | |
Gas production volume | ● | ● | ● | |
Gas production rate | X | ● | ● | |
Automatic lifting | X | √ | √ | |
Test Principle | Offline Archimedean method | Online Archimedean method | ||
Compatible batteries | Cell Type | Soft Case | ||
Cell weight | ≤1000g | |||
Cell size | ≤200*120mm | |||
Number of channels | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
Volume measurement | Range | 0~1000mL or adapted | ||
Accuracy | ±100μL | ±10μL | ||
Resolution | 10 μ L | l μ L | ||
Stability | / | ≤20uL(RT25°C,≤12h) | ||
Test temperature | RT~100C | |||
Instrument size | 600*350*1000 | 610*600*650 | ||
Instrument weight | 30kg | 40kg | 50kg | |
The change in the volume of the battery cell can be divided into hard expansion caused by side reactions and lithium insertion in the anode and gas expansion caused by processes such as formation and abuse; therefore, monitoring the volume of the battery cell can be used to study the development and optimization of its formation process, electrolyte formulation, abuse performance, etc.
Existing pain points and needs |
·No standard instrument for in-situ volume expansion test
·Based on ordinary precision balance, online stable/high-precision measurement cannot be achieved
·Single-point test based on temporary bracket, manual recording, large error
·The test process does not consider the influence of temperature, etc., and the measurement results are unreliable
Cell volume change |
·Hard expansion—caused by the expansion process of the anode during charging and lithium insertion, and byproducts such as lithium deposition
·Gas expansion—SEI formation, abuse—overcharge electrolyte oxidation, abuse—overdischarge and low power, high-temperature storage side reactions
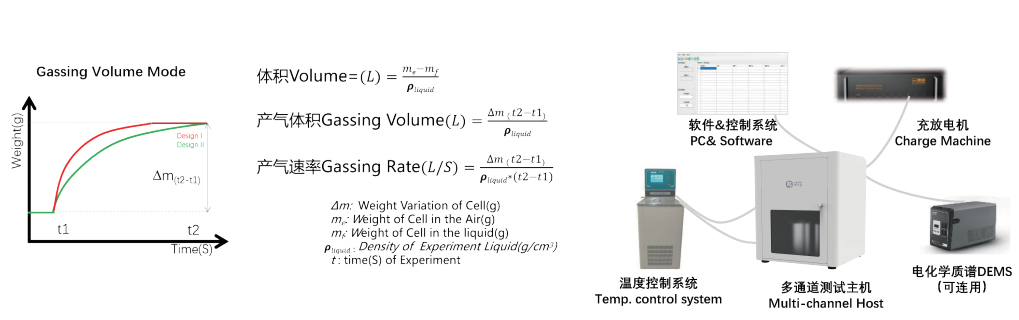
Based on the theoretical principles of Archimedes and ideal gas state equations, the change in buoyancy of the sample at a certain temperature is measured to achieve in-situ volume and gas production rate detection of the battery cell.
Industry pioneer The first multifunctional in-situ gas production measurement equipment Industry leading companies promote products | All-in-one One-stop collection of volume, temperature, humidity, electrical properties, platform, etc. Maximum 1uL resolution ±10uL range accuracy | Fully automatic measurement Fully automatic measurement of all parameters under different conditions MES connection communication (customized) | Professional data processing Single point mode and linear mode are optional Measurement data is displayed online in real time |
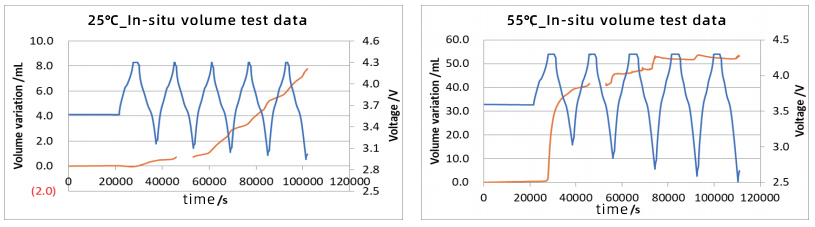
1. Evaluate the volume change of the battery cell during charging and discharging at different temperatures |
·The maximum volume expansion of the battery cell at 25°C is 7.778ml, and the maximum volume expansion of the battery cell at 55°C is 53.725ml. The maximum expansion at 55°C is 7 times that at 25°C;
·High temperature working conditions will significantly increase the volume expansion of the battery cell and significantly increase the risk, which may have a more adverse impact on the structural stability, safety and service life of the battery cell.
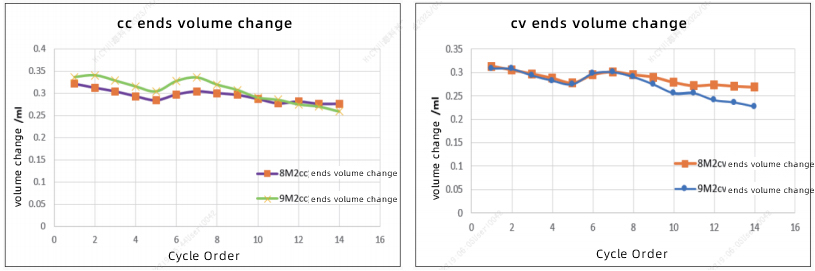
2. Battery Cell Constant Current/Constant Voltage Cycle Test |
·After 14 cycles, the capacity retention rates of batteries 8M2 and 9M2 were both above 98%. During the cycle, the maximum volume change rate of battery 8M2 fluctuated between 1.1% and 1.3%, and the maximum volume change rate of battery 9M2 fluctuated between 1.3% and 1.6%. In the cv stage after the cc cycle, the battery volumes were slightly reduced.
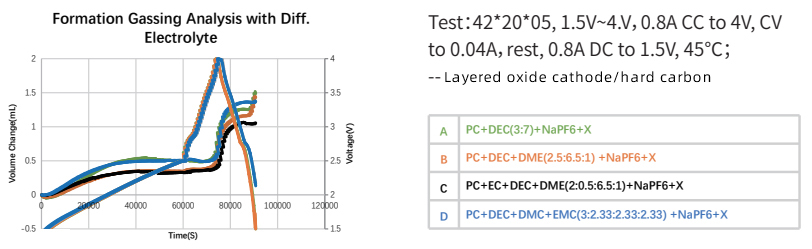
3. Study on Sodium Electrochemical Gas Production: Different Electrolyte Formulas |
· Formula C has the best effect among the four electrolyte formulas;
· The system based on layered oxide positive electrode produces almost no gas. The gas production rate increases rapidly during the high-voltage stage of charging, but is relatively small overall, indicating that the positive electrode material itself contributes little to gas production;
· Evaluate the effect of electrolyte formula on the gas production characteristics of sodium batteries, focusing on the role of solvent combination, proportion and additives.
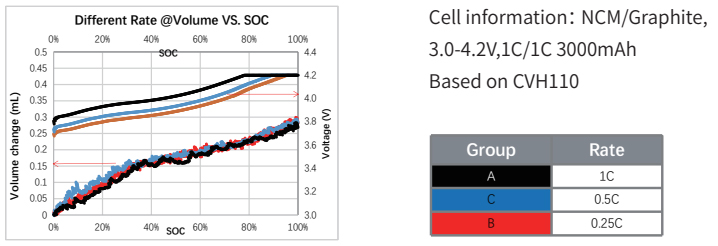
4. Hard expansion volume test: volume analysis at different magnifications |
·Analyze the volume expansion of the battery cell at different charging rates;
·For batteries with small volume differences at different charging rates, high-precision testing methods are crucial.